The White Chapel Building (former Sedgwick Centre)
Office block of 1982-4, originally with basement shopping centre, refurbished and renamed 2015-18 | Part of Whitechapel High Street south side
The White Chapel Building (former Sedgwick Centre)
Contributed by Survey of London on Aug. 15, 2019
After the formation of the Gardiner’s Corner gyratory system and the building of Central House in the mid 1960s there was a hiatus before attention turned to land use on the four-acre traffic island on the rest of the High Street’s south side. Comprehensive redevelopment was still intended in 1972 when, a much larger area southwards newly deemed obsolescent in the face of dock closures, the Greater London Council combined with Tower Hamlets Council and the City Corporation to consult about plans. This led to an exhibition in 1974 that presented three options, two of which involved rerouting traffic again, the efficacy of the gyratory already in doubt as highway planning shifted emphasis from reconstruction to traffic management. Public responses favoured the most expensive option, the pedestrianization of Whitechapel High Street with vehicle traffic rerouted along a widened Braham Street. But there was insufficient money to implement this. After further consultation with Tower Hamlets and the City, the GLC announced a much more modest approach for the island at Gardiner’s Corner in 1976. There was emphasis on providing homes, shops and a sports centre, and on ‘carefully’ controlling the amount of office building. In 1978 three large plots of land between Mansell Street and Commercial Road were offered up for development on a 99-year lease in what the GLC called an ‘important and valuable location’.1
It had become evident that offices, mainly insurance businesses, were spreading east from the City, but the GLC still urged the provision of shops and intended to impose a six-storey height limit. It also envisaged closure of the north end of Commercial Road, though instead it was the north end of Leman Street that closed. Wingate Investments Ltd, Harold Hyam Wingate’s property firm that had become a subsidiary of the builders George Wimpey and Co. Ltd, made an offer that the GLC accepted. This proposed an office block on the west end of the site, with a public-benefit sop, shops and a leisure centre further east.2
Diagonally north-west of Gardiner’s Corner in the City, the Sedgwick Forbes insurance-brokerage group had built Aldgate House on Aldgate High Street in 1971–5. This huge granite-clad block was the City’s first big deep-plan office, innovatively designed by Fitzroy Robinson & Partners, architects, with tall storey heights for services. These architects combined with what had become the Sedgwick Forbes Bland Payne Group to take forward the Wingate/Wimpey scheme and in 1980 the GLC sold all the Gardiner’s Corner lands to Avongrove Ltd, Wingate Holdings Ltd and the Sedgwick Group Ltd.
The Sedgwick Centre was built on the western plot (the site of 1–21 Whitechapel High Street) in 1982–4 as a close sibling of its City neighbour, similar even down to the heavy cornice, but bringing a scale heretofore alien to this part of Whitechapel High Street. The contractors, naturally, were Wimpey Construction UK Ltd. Clarke Nicholls and Marcel were engineers, Schmidlin, a Swiss firm, supplied windows and curtain walling, and J. Whitehead & Sons Ltd were consultants for the polished-granite cladding. The grid-like eight-storey elevations allowed for what was called ‘raised (computer) flooring’. Concealed within was an atrium and the promised shopping centre was in a basement ‘plaza’, entered, tellingly, from the west or City side; the building turned its back on Whitechapel. Underground, however, basements extended eastwards to link to Aldgate East Station and beyond to other parts of the Gardiner’s Corner site.3
The Sedgwick Group was taken over by Marsh & McLennan in 1998 and in 2001 Tishman Speyer Properties UK Ltd, a subsidiary of an American property company founded in 1978 by Robert Tishman and Jerry Speyer, bought all the Sedgwick Gardiner’s Corner properties. The Royal Bank of Scotland took occupancy of the Sedgwick Centre from 2005, the basement shopping centre closed and the building was renamed the Marsh Centre and then Aldgate Union in connection with plans for sites to the east. But Tishman Speyer sold up to RBS, which sold on. Derwent London (otherwise Derwent Valley Central Ltd) took on the former Sedgwick Centre, RBS moving out in 2015. Fletcher Priest Architects oversaw alterations and refitting and there was another rebranding in 2017, significantly against the Aldgate-obsessed grain in naming the block the White Chapel Building. A north porch was formed with signage proclaiming this, and a two-storey west pavilion went up in 2018 below more ‘White Chapel’ signage. Tech-sector occupancy was intended and achieved; the upper floors became the headquarters of the Government Digital Service, part of the Cabinet Office. The new west entrance was to have given access to lower-level use by Fotografiska, a photography centre or museum and a branch of a business founded in Stockholm in 2010 by brothers Jan and Per Broman. This was planned in 2017–19, but abandoned in 2020 on account of uncertainty generated by Brexit and Covid-19.4
-
London Metropolitan Archives (LMA), GLC/DG/PRB/35/013/056; /023/441; /025/334; /028/403; /031/055; GLC/DG/PUB/01/379/U2256; /282/U1622 ↩
-
LMA, GLC/DG/PRB/35/032/335; B/GH/LH/07/025 ↩
-
LMA, GLC/AR/BR/34/005000/169: Tower Hamlets Local History Library and Archives, Building Control files 25380–1: Tower Hamlets planninig applications online (THP) ↩
-
THP: www.publictechnology.net/articles/news/government-digital- service’s-new-whitechapel-home- revealed: British Journal of Photography, 17 Aug 2017: www.fotografiska.com/london/ ↩
Stern's Hotel, 3-5 Mansell Street
Contributed by Sheila on Nov. 1, 2018
In 1927 my father, Sam Stern, bought an empty warehouse at 3 and 5 Mansell Street, on this site. On 10 March 1928 he opened Stern's Hotel and kosher banqueting rooms in the building.
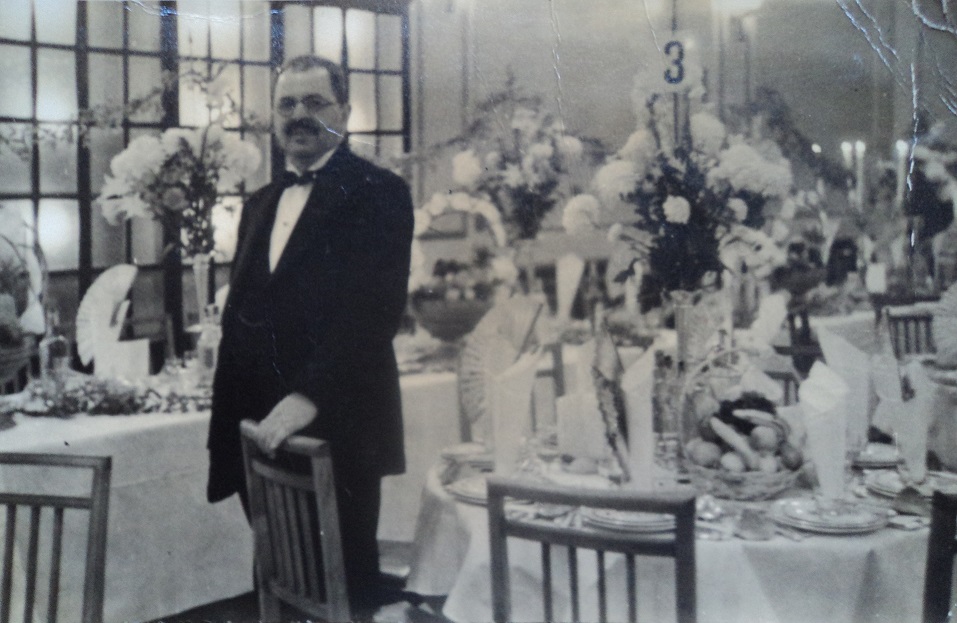

Over the years the restaurant catered more than 6,000 weddings and bar mitzvahs. In spite of the bombs the hotel remained open during the second world, providing a haven for many refugees escaping Nazism. It finally closed in 1952.

Government Digital Service
Contributed by paul on Oct. 21, 2016
The Sedgwick Centre will become the new headquarters of the Government Digital Service in March 2017.
Whitechapel High Street's south side up to the Second World War
Contributed by Survey of London on Aug. 15, 2019
Courts and alleys
Whitechapel High Street’s southern frontage was probably more or less built up in the sixteenth century before Stow reported ‘On the Southside of the high way from Ealdgate, were some few tenements thinly scattered, here & there, with many voyd spaces between them, up to the Bars, but now that street is not only fully replenished with building outward, & also pestered with diverse Allyes, on eyther side to the Barres, but to white Chappell and beyond.’1
By the late seventeenth century the diverse alleys were legion, many taking their names from the street’s numerous inns. They were generally built up with small cottages, also a few substantial houses, ostensibly domestic spaces being no doubt also in use for industrial purposes. From the later eighteenth century humble housing on courts and alleys gradually gave way to purpose- built commercial premises such as workshops or warehouses. Newly formed Pavement Commissioners for the High Street settled its numbering in August 1771. It has stayed essentially unchanged since. To account for the courts and alleys, running from west to east, it will help orientation to use that street numbering consistently, if sometimes anachronistically.2
By 1674 Irish Court was behind Nos 4–5, holding seven houses, two with seven and eight hearths. These were replaced with warehousing around 1780 and the court survived up to the 1940s when the area was bombed. White Hart Court Yard, behind No. 10 and two other eight-hearth properties on the High Street, had nineteen houses in the 1670s, one of twelve hearths pertaining to Elizabeth, Lady Mellowes (d. 1692), five others having eight and nine hearths. Eagle and Child Alley with seventeen one- to four-hearth houses in the 1670s later became Horns Yard or Court and was largely cleared in the 1790s. Half Moon Court, between Nos 17 and 18 and still enduring at its south end, held twenty-one houses in 1675, all of three hearths except that of Thomas Peake who had eleven hearths; by 1800 Half Moon Court was recorded as having only eleven small houses. Peacock Court had eighteen one- to six-hearth houses in the 1670s, but then disappears from reckonings. Elephant Court’s eight-hearth property was probably an eponymous inn, held in 1675 by ‘Lockworth & Cannon etc’, otherwise the place had just four two- and three-hearth houses. Twelve houses lasted into the 1750s on what became Elephant & Castle Court by 1841, not long before its demise. Swan Court or Yard lay between Nos 20 and 21 and had about twelve confined and back-less small houses through the eighteenth century up to 1874–5 when they were replaced with a Pickford’s goods and parcel depot. Red Lion Street intersected on the site of No. 31 from around 1685.
Continuing eastwards, by the 1670s Whittington’s Cat Alley was between Nos 34 and 35 with ten one- to three-hearth houses, close to Greyhound Alley, four one- and two-hearth houses, Tobacco Pipe Alley, three one- and two-hearth houses, and Window Alley, ten one- to four-hearth houses. Cock Alley appears to have been renamed or redeveloped in the late eighteenth century as Barley Mow Court, stitched in behind Nos 38–40 with five to eight small houses. Plough Alley, between Nos 44 and 45, had nineteen one- to four-hearth houses in the 1670s, but Plough Street replaced it around 1700. Baptist’s Head Alley, with seven one- to three-hearth houses, and Clarke Alley, seven one- and two- hearth houses, were recorded in the 1670s, apparently succeeded by Woolsack Alley and Darts Alley between Nos 47 and 48.
Drum Alley had twenty-one and King’s Head Alley nine one- and two-hearth houses in 1675. Drum Court or Yard between Nos 50 and 51 had ten small houses in 1790. Last Alley, with seventeen one- to six-hearth houses in the 1670s, appears to have become Dyers Yard between Nos 51 and 52 with only four small houses in 1800. Bull (or Bulke) Stake Alley, between Nos 58 and 59, where John James (d. 1661) led a congregation of Seventh Day Baptists, had eighteen one- to three-hearth houses in the 1670s, but only five houses in 1800. Finally, there was Hatchet Alley (later Spectacle Alley, now Whitechurch Passage), off which lay Adam and Eve Court.
Some of these houses, many of which would have been timber built and weatherboarded, survived into the twentieth century, as on the west side of Half Moon Passage where seven very small cottages stood behind No. 20 and in front of a brass foundry.3
Public houses
The names of the courts and alleys have given some indication of the High Street’s public houses, recorded here again from west to east. The Three Tuns was at 1 Whitechapel High Street by 1740. It was modestly rebuilt in brick in 1922–3 to plans by William Stewart, architect, for Mann Crossman Paulin of the Albion Brewery. It came down in the 1960s.4
The White Hart, on the site of Nos 9–10, was present by the 1670s and may well have had much earlier origins. To its rear was the largest and longest-lived inn yard on this side of the High Street, comprehending not just stabling but once also many dwellings with some substantial houses (see above). To the front there was a five-bay eighteenth-century building with a central pediment. The pub, sometimes the White Hart and Three Tobacco Pipes, appears to have closed before 1800, after which the White Hart name settled on the other side of the High Street. The Mercers Company owned both the High Street’s White Hart properties. James Spalding (d. 1780) took No. 9 by 1750 as premises for a grocery and tea-dealing business that became Spalding, Clarence and Millikin after he was joined by William Clarence and Halley Benson Millikin (_c._1750–1826). Its large back warehouse was built in the 1780s, possibly also the date of the front range. Spalding was a partner in sugar- refining businesses and Millikin was himself a sugar refiner elsewhere after 1800.5 Peter Simmonds, who had been the White Hart’s last innholder, carried on as a keeper of livery stables in the yard. These continued into the 1850s, followed by a wholesale provisioning depot up to the 1880s. The pedimented front range survived in reconstructed form up to the 1960s.6
The Horns at No. 16, possibly preceded thereabouts by the Eagle and Child in the late seventeenth century, appears to have been established around 1836 by James Thomas Reynolds in what would then have been a new building. It continued till the 1920s.7
The White Swan Inn (later just the Swan) at No. 20 was present by the eighteenth century and into the 1920s. The Elephant and Castle at No. 23, likely to have had early origins further west, closed in the 1860s, but had a second life, reappearing from the 1950s to the early 1980s. The Talbot Inn, at No. 25 by the 1690s, was a large establishment in a six-bay four-storey and attic eighteenth-century building. It closed sometime after 1810 and William Coates & Co., City wine merchants, took the premises around 1825. Coates & Co. extended to the Elephant and Castle and rebuilt Nos 22–23 in 1869–71 with James Harrison as their architect, erecting extensive warehousing to the rear. For a time Nos 22–23 were Frederick King’s retail wine stores, but the group at Nos 22–26 continued as W. Coates & Co., then Percy Fox Ltd, all the while wine stores. Retention and refurbishment of the front buildings at Nos 24–26 was intended in 1978, but demolition ensued in the early 1980s.8
The Red Cow Inn at No. 26 was a short-lived establishment of the eighteenth- century’s middle decades. Next east at No. 30, later No. 29, was the Red Lion, an inn of much greater longevity that was acquired and rebuilt in 1682–5 to allow formation of the eponymous street through its site. It was in 1810 the birthplace of William John Little (1810–1894), son of John and Hannah Little, the pub’s proprietors. Afflicted with a club foot from infancy, Little rose to renown as an orthopaedic surgeon. The pub was rebuilt for the last time in 1903 as the Old Red Lion,a big blowsy corner boozer with ample architraving in four storeys. Its ground-floor front became an entrance to Aldgate East Station in 1937–8, but the pub continued through to the 1990s and was only demolished around 2004.9
The Whittington & Cat at No. 35, of seventeenth-century or earlier origins, was cleared in the 1860s. No. 36 was the Bunch of Grapes Coffee House by 1760, converted to be a wine and brandy merchants by 1780. The Barley Mow was at No. 39 by 1730, but gone before the end of the century. The Hat & Plough was at No. 44 by 1760 and was raised in 1853 only to be displaced in 1874.10
The Cock existed as ‘the Cok’ in the late 1450s when Alice, who had been Simon Cok’s wife, went to law against Thomas Hosewyf, the property owner. It may have had its origins on a site further west, given the presence of Cock Alley, but by the 1830s it was at No. 45, east of Plough Street, where there had been a brandy merchant since before 1770. The Cock was rebuilt in 1872–3 extending back to 9 Commercial Road, to designs by W. W. Browne, architect, with Thomas Ennor as builder. F. Beger took an eighty-year lease and William Henry Price was the first licensee. It kept going into the 1920s and the building was not demolished until 2008.11
The King’s Head was on the site of No. 49, run by Thomas Redwood in 1730. It became the Yorkshire Gray in the 1740s and was rebuilt at Nos 48–49 in 1875, further alterations in 1884 being to plans by Wilson, Son & Aldwinckle. The Yorkshire Gray continued up to the early 1960s.12
The Bull and Stake, run by William Gibbons in 1730, was perhaps renamed the White Horse and Leaping Post, which was on the site of No. 58 by 1750. Later becoming the Horse & Leaping Bar, it was rebuilt in 1892–4 for and by Francis Gill, a publican and builder who had a run-in with the LCC, which enforced demolition of parts of his new building. The pub closed in the 1930s. Associated livery stables across Bull Stake Court at No. 59 were newly formed in 1815.13
Other early commerce
Through the eighteenth century the thoroughly commercial south side of Whitechapel High Street housed numerous butchers, grocers, cheesemongers and oil and colourmen. The notable clutch of butchery with slaughterhouses just outside the City boundary at Nos 2–7 was an extension of what was known as Butcher Row on the south side of Aldgate High Street, present by the late sixteenth century and continuing, though diminished, into the 1950s.14
Thomas Quarill, a substantial oil and colourman, a Paving Commissioner and Governor of the London Hospital, had significant premises at No. 11 by 1740 at which Luke Alder succeeded. Robert Buttery (_c._1710–1793) was a seedsman and corn chandler at No. 15 from the 1750s. After the death of his wife in 1773, he owned five High Street properties and land in Irish Court and retired to Hertfordshire. His premises were recast in the early nineteenth century.15
William Claxton, a china, pot and glass seller, had premises at No. 24 from the 1760s that were identified as a ‘Staffordshire Warehouse’ in 1800. Isaac Colnett (d. 1801) was a blacksmith, ironmonger and tiresmith at No. 27 from the 1750s.16
John Ellison, a druggist, was at No. 33 from the 1750s to his death in 1790. A large building went up for his successor, Jonathan Jordan. Redbourn Tomkins (_c._1711–1792), a Baptist and another hospital governor, was a successful tallow chandler at No. 42 from the 1740s.17
Francis Laurson (d. 1777), a scrivener who lived in West Ham, had offices at No. 51 by 1740 up to his death. He was succeeded by his clerk, William Argill, who was West Ham’s Vestry Clerk and who styled himself an attorney. The late- seventeenth- or early eighteenth-century three-storey brick house with a centre-staircase layout at No. 51 stood into the 1890s, weather-boarded and timber-framed on its return to Drum Yard.18
William Hamilton, an undertaker and Treasurer of the High Street’s Paving Commissioners, was at No. 54 in the mid eighteenth century. Henry Mowtlow (_c._1664–1740), a clock maker, whose surviving pieces fetch handsome sums, and parish clerk, had been at No. 56. Joseph Gwyn (d. 1773) was a carpenter and coachmaker at No. 60 from the 1740s.19
1–53 Whitechapel High Street: 1840s to 1930s
Parts of the south side of the High Street began to be sacrificed for the sake of better road circulation. Nos 31–34 were cleared in the 1840s for the widening of Red Lion Street as the north end of Leman Street, a crucial link in the road north from the docks that continued as Commercial Street. The resultant new major junction, also the middle of the Haymarket, had its centre marked in 1853 by an obelisk that had been a part of the Great Exhibition, purchased by the parish of Whitechapel.20
Nos 35–43 were cleared for the westwards extension of Commercial Road that was approved in 1865 and carried through in 1869–70. The junction was soon further transformed. Tramways tore up the road from 1888; electrification and overhead lines followed in 1906–7. The obelisk came down in 1913 and the Haymarket closed in 1928.21
Meanwhile numerous High Street properties were redeveloped. A shophouse rebuilding at No. 50 that appears to have escaped visual record, having been reconstructed in 1929, was lavished with unusual praise in 1858 in The Builder, a whole column’s worth, for avoiding the monotony of then standard Italianate dressings, instead favouring simple red-brick and functional dressings. The architect was the otherwise little-feted Charles Bennett Arding.22
The Commercial Road’s extension opened up development sites east of the new junction. Gardiner & Co., Glasgow clothiers and Army contractors, took the plum triangular corner plot in 1872 for the erection of a department store. J. H. H. and J. Gardiner’s London agent was Thomas Corbett, and the firm employed George Aitchison junior, whose practice was strongly east London based, to be its architect. Whitechapel High Street’s largest shop resulted at 31–35 Whitechapel High Street and 1–5 Commercial Road. When it opened in 1874, Gardiner & Co. secured a contract worth £150,000 to supply the Metropolitan Police (10,000 officers) and government dockyards with clothing for five years. This austerely classical department store was Whitechapel High Street’s dominant building for a century, prominent and markedly up-scale for its location, which became known as Gardiner’s Corner, a firm print on Whitechapel’s sense of place. Continuing to specialise in military uniforms and children’s clothing, Gardiner’s was extended eastwards along Commercial Road and then in 1899 raised by two storeys and given a prominent clock turret that rose to 130ft, the top-heavy result wrecking Aitchison’s proportions. John Wallis Chapman (1843–1915) was the architect of this addition, Holliday & Greenwood the builders. By this time the establishment called itself ‘The Scotch House’. Gardiner’s closed in 1971 and the building was destroyed by a spectacular fire in 1972.23
Immediately eastwards, No. 44 (formerly the Hat and Plough and keeping the old numbering) was redeveloped in 1874 as the Aldgate Turkish Baths, again with George Aitchison as architect. Run by James Forder and Henry Nevill, this followed on from an earlier establishment of theirs at London Bridge. Of four storeys and in line with Gardiner’s, it had one entrance for men on the High Street and another for women to the rear at 7 Commercial Road. It was a success and the firm opened other Turkish Baths, as at New Broad Street (Bishopsgate Churchyard) in 1895, which survives. From 1908 the chain of premises was incorporated as Nevill’s Turkish Baths Ltd and the Whitechapel establishment endured up to the Second World War. The building was demolished in the 1970s.24
Across Plough Court was the Cock (see above), also rebuilt in the 1870s, and then No. 46, rebuilt in 1883 for E. R. Goodrich to designs by John Hudson, architect, and extending to 11 Commercial Road at the back. Stepney Labour Exchange was here for a few years around 1910, moving to Nos 59–60 in the 1920s. No. 47 was rebuilt with 13 Commercial Road in 1921–2 as a factory for Sam and Joseph Hyman Tym, underclothing manufacturers. Nos 45–47 stood until 2008. Nos 51 and 52–53 were rebuilt in 1896–7 for F. G. Debenham and J. Nathan respectively. Harvey Dyball was the architect at No. 51, and Nos 52–53, intended as a shop and dwelling rooms, were soon taken by the St Ursula Working Girls’ Club.25
Returning to the west, Nos 11–14 and buildings behind on White Hart Yard were cleared for the formation of the Metropolitan and Metropolitan District Railway underground extension to Whitechapel in the early 1880s. The site, a short distance south-east of Aldgate East Station, was left open either side of an access bridge to ventilate the steam-powered railway below. Upon electrification of the line, Edwin Bell, a builder trading as Bell & Co., acquired the site and in 1907–9 developed it with Aldgate East Chambers, a broad six-bay and four-storey shop, office and workroom speculation with a central arch to maintain access to White Hart Yard. Undeterred by a fine for the use of poor-quality bricks, Bell introduced a ‘Bioscope Exhibition Room’ or cinema at No. 12 in 1910, extended to Nos 9–10 and 16 in 1909–11 and enlarged further to the rear for workshops and showrooms in 1913–15. Early tenants were mainly tailors and furriers, with a restaurant and the Scottish Sanitary Laundry alongside. The back buildings were destroyed and those to the front damaged by a bomb strike in the Second World War. No. 7 had been separately rebuilt with a gable front in 1907, to plans by W. A. Lewis for William Gower, a fishmonger. John Hawkins & Son, wholesale tea dealers and grocers, were at Nos 17–19 from the 1840s until clearance in the early 1960s, though by 1920 No. 19 had been given up to Jacob Levy, a cycle agent who soon branched into importing jazz records, sold from Levy’s at this address into the 1950s. No. 17 became a branch of Tesco Stores Ltd by 1960, shortly before clearance.26
Redevelopment at the High Street’s west end followed the widening of Mansell Street on its City side and the First World War. Nos 2–4 were rebuilt in two parts in 1922–3, at the same time as the adjoining Three Tuns (see above), as four-storey and attic rag-trade workshops for Scales & Leuw, meat salesmen, and Mrs Ray Mercado, a confectioner, with H. A. Porter as architect. There were additions in 1928 for Skolnick, Lipton and Guttridge Ltd, hosiery manufacturers, by when blouse-making and the London Board of Shechita were also housed. No. 6 was a shophouse with a billiard hall of 1923–4. Hosiery and millinery were strong presences here up to clearance in the 1960s.27
A boot and shoe warehouse at Nos 27–28 was sold at auction in 1920 and redeveloped to be a branch of Lloyd’s Bank in 1922–3, also occupied by the Sun Life Assurance Company. This was a restrained three-bay neo-Georgian building, a minor example of the stylishness brought to Lloyd’s Bank’s architecture by Horace Field. It was demolished around 2004.28
-
John Stow, A Survey of London, 1603, ed. C. L. Kingsford, 1908, vol.1, p.127 ↩
-
Tower Hamlets Local History Library and Archives (THLHLA), L/SMW/C/2/1 ↩
-
William Morgan's map of 1682: John Rocque's map of 1746: Richard Horwood's maps of 1799 and 1813: The National Archives (TNA), hearth-tax returns 1674–5: Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (ODNB) sub James: London Metropolitan Archives (LMA), Land Tax Returns (LT); District Surveyors Returns (DSR); Collage 3455: Ancestry ↩
-
Post Office Directories (POD): LMA, Collage 121852; LT; DSR ↩
-
LMA, MR/LV/8/68; CLC/B/192/F/001/MS11936/360/556370; 11936/447/828725: LT: Mercers Company Archives, Dean Colet Estate Plans, 1821–3, plate 1; 1823–34, plate 33: Museum in Docklands, Shadwell portfolio, folder 7, sheet 3: information kindly supplied by Andrew Byrne: TNA, PROB11/1064/165: Bryan Mawer's sugar-refining database: LMA, Collage 121781 ↩
-
POD: Goad insurance maps: DSR: LMA, Collage 121852 ↩
-
LT: POD: information supplied by Stephen Harris ↩
-
LT: POD: The Builder, 23 Oct 1869, p.854: DSR: Goad, 1887, 1924 and 1960: LMA, Collage 121843,167445; P93/MRY1/091, p.144; GLC/DG/PUB/01/28/U1622 ↩
-
TNA, C5/99/23; C7/58/2: LMA,MR/LV/6/79: LT: ODNB sub Little: DSR: POD ↩
-
LMA, MR/LV/7/49; MR/LV/8/68: LT: POD ↩
-
TNA, C1/26/357: LT: The Builder, 20 July 1872, p.574: DSR: POD: LMA, LMA/4673/D/09/02/002, f.51; Collage 121955: information supplied by Stephen Harris ↩
-
DSR: The Builder, 3 May 1884, p.629: LT: POD ↩
-
LT: LMA, MR/LV/05/026; MR/LV/06/079: THLHLA, P/HLC/1/14/6: POD: London County Council Minutes (LCC Mins), 28 Feb, 13–14 June and 3 Oct 1893, pp.200,613,649,930: information supplied by Stephen Harris ↩
-
LT: POD: LMA, P93/MRY1/091, p.23: Historic England Archives, Mayson Beeton Collection J1001141: John Strype, A Survey of the Cities of London and Westminster, vol.1/2_, 1720, p.27: Daniel Defoe, _A Journal of the Plague Year, 1722 (edn 1969), p.171 ↩
-
LT: TNA, PROB11/1229/237: Hertfordshire Record Office, DE/B737/T42: General Evening Post, 14 March 1793: Derek Morris, Whitechapel, 2011, pp.58,143 ↩
-
TNA, PROB11/1357/258: LT ↩
-
TNA, PROB11/1189/161: LT: Ancestry ↩
-
LT: TNA, PROB11/1036/57: Public Advertiser, 15 Jan 1783: THLHLA, Building Control file 41778 ↩
-
TNA, PROB11/702/484; PROB11/984/309: LT: Antiques Trade Gazette, 2 Feb 2004: Morris, 2011, p.15 ↩
-
The Builder, 19 Feb 1853, p.116 ↩
-
Metropolitan Board of Works Minutes (MBW Mins), 10 Feb 1888, p.265: LMA, Collage 231467–8, 231472, 231494, 231498 ↩
-
The Builder, 11 Sept 1858, p.613: DSR ↩
-
DSR: MBW Mins, 10 May 1872, p.676; 22 May 1874, p.632; 13 May 1881, p.790: TNA, ED27/3242: POD: Daily Telegraph and Courier, 23 April 1874: Glasgow Herald, 12 Nov 1874: LCC Mins, 27 June 1899, p.950: Financial Times, 24 May 1976 ↩
-
MBW Mins, 1 April 1874, p.449: POD: The Globe, 15 April 1875: Malcolm Shifrin, Victorian Turkish Baths, 2015 ↩
-
DSR: POD: The Builder, 13 Jan. 1883, p.63: MBW Mins, 25 June 1880, p.898: THLHLA, Building Control file 41778: LMA, Collage 121954–5 ↩
-
Transport for London Group Archives, LT000612/030: DSR: POD: LCC Mins, 23 April and 18 June 1907, pp.842,1278; 11 Oct 1910, p.521: LMA, GLC/MA/SC/03/1336; Collage 121846,121852–4 ↩
-
DSR: Goad, 1924: LMA, Collage 121852: POD ↩
-
DSR: POD: Estates Gazette, 21 Feb 1920, p.268: Timothy Brittain- Catlin, ‘Horace Field and Lloyds Bank’, Architectural History, vol.53, 2010, pp.271–94 ↩
Gardiner's Corner reconstruction
Contributed by Survey of London on Aug. 15, 2019
Traffic was an abiding headache on Whitechapel High Street. It had been for centuries and the confluence of the Leman Street–Commercial Street axis with the west end of Commercial Road from the 1870s exacerbated problems on critical routes to and from the City, as always, and now also to and from the docks. The cessation of the Haymarket in 1928 reduced congestion, but unquestioning acceptance of predictions of growth in car usage and the wider contexts of highway planning soon came into play. The influential Royal Academy traffic plan for London of 1938 by Sir Charles Bressey and Sir Edwin Lutyens proposed three concentric ring roads, including an inner arterial ‘loopway’ round the City. This found its way into the _County of London Plan _of 1943 as an ‘A’ or inner (but sub-arterial) ring road with a great pentagonal roundabout at the strategically important intersection at Gardiner’s Corner. Already in 1941 Stepney Borough’s Engineer and Surveyor, B. W. Stuttle, had promulgated London’s first reconstruction plan for his borough, advocating the use of existing road networks, against the wider new network thrust of the County plan. After the war, the Ministry of Transport advanced plans for the ‘A’ ring road as arterial. The Gardiner’s Corner roundabout, now being drawn as a hexagon, was incorporated as a key element of the London County Council’s reconstruction scheme for the Stepney and Poplar Comprehensive Development Area.1
By 1952 the LCC’s Highways Committee had reshaped the roundabout to be an elongated rectangle, keeping somewhat to existing roads to reduce costs. Further revised by 1955 with a schematic model, this approach kept Whitechapel High Street intact, with Braham Street and Beagle Street widened to the south, the west end of Commercial Road diverted northwards through 50–54 High Street (and Drum Yard) for a short east end, and Mansell Street as the west end. By 1957 further parts of the war-damaged western part of the intended island (Nos 1–21) had been cleared. As CPOs were issued, zoning intentions were for future use here to mix warehousing, offices, light industry and shopping. In 1960 the LCC Architect’s Department under Hubert Bennett prepared schemes for three pedestrian subways: at the west end of the High Street; at the Red Lion for Aldgate East station; and at the new end of Commercial Road. These, with ramps as well as stairs, were to keep people on foot from slowing down traffic, though lip service was paid to safety. A new model envisaged a flyover across the island’s eastern parts to link Commercial Road directly to the High Street’s west end, the west part of the island modelled as having three north–south slab blocks on a podium and the east part (Drum Yard) a Miesian tower, evidently ephemeral ideas at the time.2
Traffic volumes had almost doubled since the war by 1964 when the highway and subway works were at last begun to designs prepared under the LCC’s Chief Engineer, Peter F. Stott. Completed in 1966, the work was done by Fitzpatrick & Sons (Contractors) Ltd. The overall cost of £1,500,000 for the project was split equally between properties and works. Road circulation was clockwise with Whitechapel High Street made a one-way road for eastbound traffic, railings forcing pedestrians to use the subways. The cleared western part of the island was put to use as a car and lorry park.3
-
London Metropolitan Archives (LMA), LCC/CL/HIG/02/149: The Times, 17 May 1938, pp.33–38: J. H. Forshaw and Patrick Abercrombie, County of London Plan, 1943, pp.51–4,147 and plate 4: D. L. Munby, Industry and Planning in Stepney, 1951, pp.378–84: Kathryn A. Morrison and John Minnis, Carscapes: The Motor Car, Architecture and Landscape in England, 2012, pp.342–8: information kindly supplied by Simon Pepper ↩
-
LMA, LCC/CL/HIG/02/103; COL/PL/01/165/C/025; SC/PHL/02/0677 (55/2/TP/46F/0221-5 and 60/3362–6) ↩
-
LMA, GLC/DG/PTI/P/05/041; GLC/DG/PUB/01/231/U0963; COL/PL/01/165/C/026–7 ↩

Aldgate Place under construction in 2016
Contributed by Derek Kendall

Construction site at Aldgate Place, August 2017
Contributed by Derek Kendall

Aldgate Place under construction, August 2017
Contributed by Derek Kendall

Site of the former Gardiner's Corner, August 2017
Contributed by Derek Kendall

Sedgwick Centre
Contributed by Derek Kendall
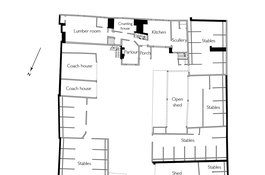
White Hart Yard behind 8–13 Whitechapel High Street, c.1825
Contributed by Helen Jones